| ISETHIONIC ACID | ||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 107-36-8; 51694-03-2 |
| ||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 203-484-3 | |||||||||||||||
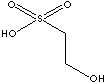
| FORMULA | CH2OH·CH·SO2OH | |||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 126.13 | |||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | 2-Hydroxyethanesulfonic acid; (2-Hydroxyethyl)sulfonic acid; | |||||||||||||||
| 2-Hydroxyethansulfonsäure (Dutch); ácido 2-hidroxietanosulfónico (Spanish); Acide 2-hydroxyéthanesulfonique (French); Ethanolsulfonic acid; Hydroxyethylsulfonic acid; | ||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
liquid | |||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | ||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 100 C | |||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
soluble | |||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR PRESSURE | ||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2 ; Flammability: 0; Reactivity : 0 | |||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
| |||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||
Isethionic acid,
the ethyl chain sulfonic acid containing hydroxy group,
is a water soluble, strongly acidic liquid; used in the manufacture of
mild, biodegradable and high foaming anionic surfactants
which provides gentle cleansing and soft skin
feel.
Isethionic acid
is the trivial name for 2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid
which is the parent compound of sodium isethionate.
Sodium isethionate is prepared by the reaction of ethylene oxide with sodium bisulfite
solution. It is used as a key raw material in the manufacturing of Igepon type surfactants
which are ethanesulfonated detergent bars. Igepon type surfactants
include:
|
||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
liquid | |||||||||||||||
|
CONTENT |
80.0% min | |||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS |
| |||||||||||||||
| UN NO. |
| |||||||||||||||
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF IONIC SURFACTANTS |
||||||||||||||||
|
Ionic surfactants which contain hydrophobic hydrocarbon group connected with one or several hydrophilic groups dissociate into a positively charged cation and a negatively charged anion in an aqueous solution. If the head is negatively charged to carry the surface active properties, it is called anionic surfactant, whereas a positively charged head is the carrier of the surface active properties in cationic surfactants. Typically cationic surfactants are based on the nitrogen atom carrying the cationic charge such as amine and quaternary ammonium product. Cationic surfactant is considered to be poor cleaners but it contributes to the fabric softening, the disinfecting properties, and the grease-water interfacial tension reducing. Cationic surfactants include quaternary ammonium compounds, amines (primary, secondary, tertiary, diamines, polyamines, amine salts), imidazoline compounds, betaine compounds, and esterquats. Anionic surfactant is the widely used type of surface active agent for laundry detergents, liquid cleaners and shampoos due to excellent cleaning properties particularly effective at oily soil cleaning and oil/clay soil suspension. Anionic surfactants are deactivated in many hard water. To prevent deactivation, builders should be dosed. Anionic surfactant is used as a emulsifier in cosmetics, tooth paste, cream, shampoo, and acrylic binder. Common soap is an anionic surfactant. Carboxylate, sulfate, sulfonate and phosphate are the polar groups in anionic surfactants. Anionic surfactants include alkyl benzene sulfonate, fatty acid salts, sodium lauryl sulfate, alkyl sulfate salts, sodium lauryl ether sulfate, alpha-olefin sulfonates, phosphate esters, sulphosuccinates, alkyl phenol ether sulfates, and isethionates. |
||||||||||||||||